12. UML Diagrams
Unified Modeling Language (UML) helps us visualize, design, and document software systems. By learning UML, you gain a powerful tool to communicate complex ideas clearly, structure your code effectively, and collaborate better in teams. Whether you're planning a new application or improving an existing one, UML supports thoughtful design and reduces misunderstandings.
12.1 Class Diagram
Class diagrams show the static structure of a system - classes, their attributes, methods, and relationships.
12.1.1 Example: Online Shop System
┌─────────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ Customer │ │ Product │
├─────────────────────┤ ├─────────────────────┤
│ - id: int │ │ - id: int │
│ - name: string │ │ - name: string │
│ - email: string │ ────────│ - price: double │
├─────────────────────┤ │ - stock: int │
│ + addToCart() │ ├─────────────────────┤
│ + checkout() │ │ + getPrice() │
│ + getOrders() │ │ + updateStock() │
└─────────────────────┘ └─────────────────────┘
│ │
│ │
│ │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ Order │ │ OrderItem │
├─────────────────────┤ ├─────────────────────┤
│ - id: int │ │ - quantity: int │
│ - date: DateTime │ ────────│ - subtotal: double │
│ - total: double │ ├─────────────────────┤
├─────────────────────┤ │ + calculateTotal() │
│ + calculateTotal() │ └─────────────────────┘
│ + addItem() │
└─────────────────────┘
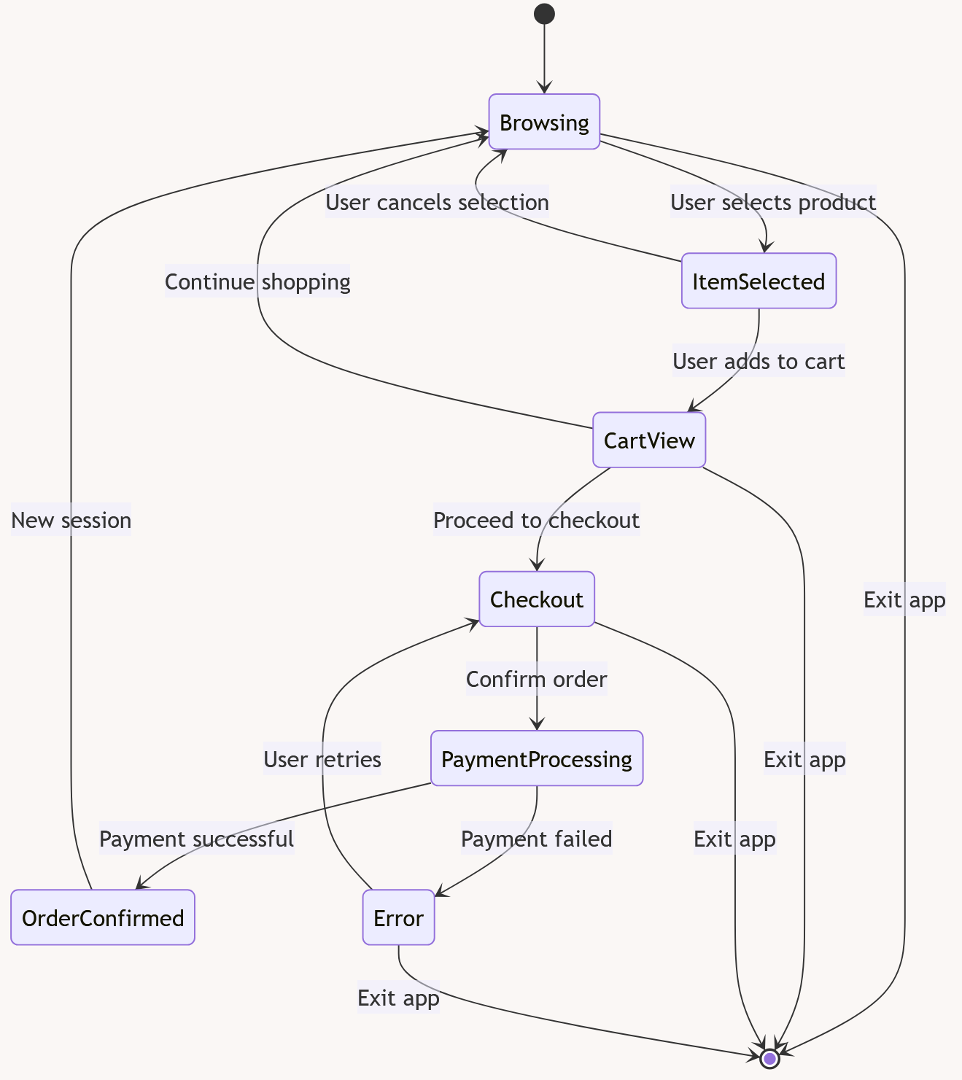
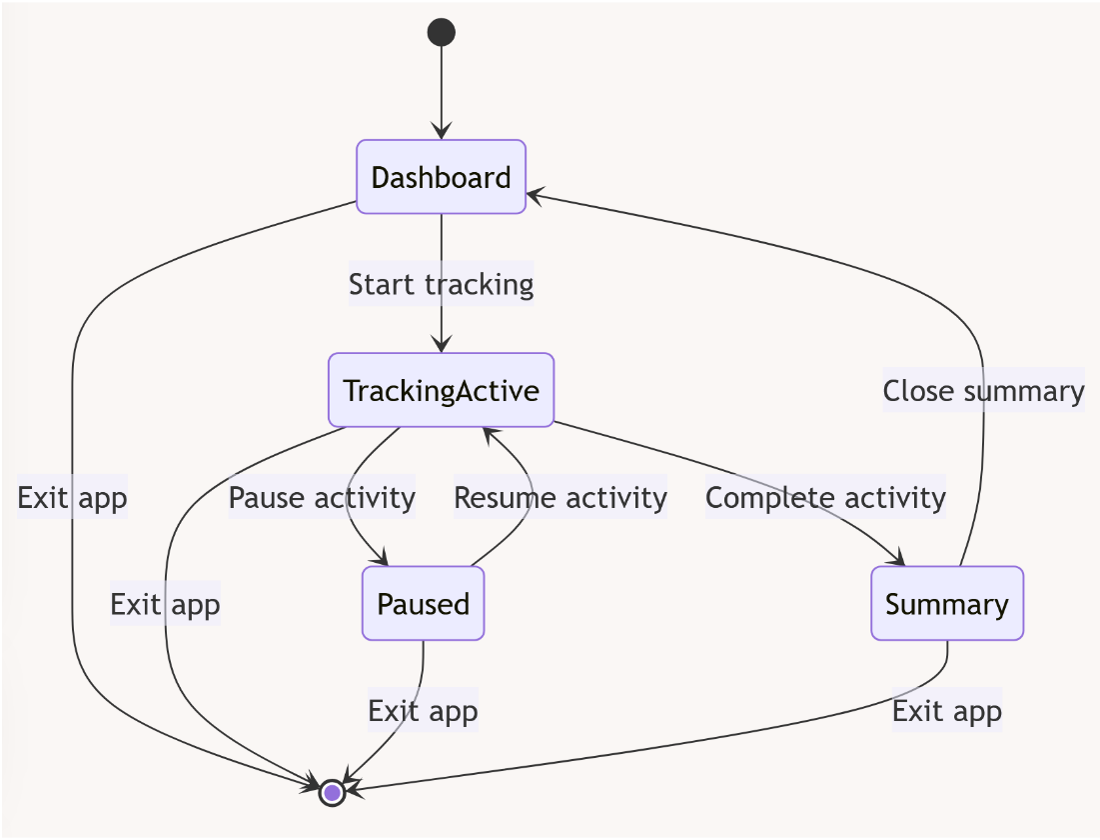
12.2 State Diagram
A state diagram shows how an object behaves over time by visualizing its possible states and transitions. It's useful when modeling systems that react differently based on their current condition, like traffic lights, user sessions, or device modes.
- Focus: Lifecycle of an object
- Shows: States, transitions, events, and conditions
Example: Traffic Light
stateDiagram
[*] --> Red
Red --> Green : Timer
Green --> Yellow : Timer
Yellow --> Red : Timer
Problems with this simplified traffic light
- What happens if a light bulb fails? Or a power outage? This model doesn’t account for fail-safes or maintenance modes.
- It assumes an immediate start in "Red". In reality, systems may require an initialization phase.
Below you will find more complicated examples
12.3 Sequence Diagram
A sequence diagram shows how objects interact in a particular scenario by emphasizing the order of messages exchanged over time. It’s ideal for understanding workflows, like placing an order or logging in.
- Focus: Communication between objects
- Shows: Objects, lifelines, messages (calls), and return values
Example: Online Order Process
sequenceDiagram
participant Customer
participant WebUI
participant OrderService
participant PaymentService
participant Database
Customer->>WebUI: placeOrder(item)
WebUI->>WebUI: "UI: Processing order"
WebUI->>OrderService: createOrder(customer, item)
OrderService->>OrderService: "OrderService: Creating order"
OrderService->>PaymentService: processPayment(customer, 99.99)
PaymentService-->>OrderService: true
OrderService->>Database: saveOrder(customer, item)
OrderService->>OrderService: "OrderService: Order created successfully"
12.4 Entity-Relationship Diagram (ER Diagram)
An Entity-Relationship (ER) Diagram is a visual tool used in database design to represent:
- Entities (e.g., Student, Course)
- Attributes (e.g., name, credits)
- Relationships (e.g., a student enrols in courses)
ER diagrams help model the structure of a database logically, making it easier to understand how data is connected and organized.
Example: University System
erDiagram
STUDENT ||--o{ ENROLMENT : enrols
COURSE ||--o{ ENROLMENT : has
PROFESSOR ||--o{ COURSE : teaches
STUDENT {
int student_id PK
string name
string email
}
PROFESSOR {
int professor_id PK
string name
string department
}
COURSE {
int course_id PK
string title
int credits
int professor_id FK
}
ENROLMENT {
int enrolment_id PK
date enrol_date
string grade
int student_id FK
int course_id FK
}
- Students can enrol in many Courses, and each Course can have many Students. This many-to-many relationship is managed via the ENROLMENT table.
- Professors teach Courses. Each course is taught by one professor (one-to-many).
- The ENROLMENT table includes
- A foreign key to STUDENT
- A foreign key to COURSE
- Additional attributes like enrol_date and grade